When the quenching workpiece is interrupted, the surface of the workpiece is grayish white, and then the grayish white color of the surface is converted into color. Due to the high temperature of the surface of the plate, the surface is oxidized after being exposed to oxygen in the air, and the thickness of the plate is thin. It is considered that the center temperature of the plane surface is approximately the same as the center temperature of the plate thickness direction. The change of the oxidation color of the surface clearly shows the temperature distribution of the plate. See Figure 5, where the four plate angles of Zone 1 are the lowest, and finally The oxidation color is light yellow, the change is not big, the temperature in the excessive zone 2 is slightly higher, and the white color immediately from the furnace is changed into grass yellow, yellow, and purple, and the color from the edge to the plane of the plate plane is gradually deepened, and the highest temperature region 4 is released. The color quickly turns blue and black.
Approximate correspondence between surface color and surface temperature: light yellow 220 ° C, grass yellow temperature about 250 ° C, purple temperature about 280 ° C, blue temperature about 300 ° C.
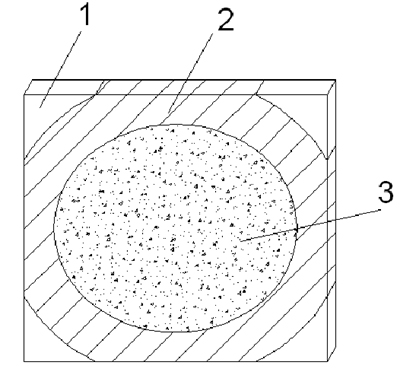
Figure 6. Temperature distribution of the sheet
Fourth, the analysis of the deformation law of the board
The deformation of the plate is the same as the formation of all the quenched parts. It comes from the thermal stress and the structural stress. Due to the high hardenability of these materials, the plate is quenched after the quenching, but how to understand the quenching The change in stress distribution during cooling. A model can be introduced to explain and analyze Figure 6 as a cross section of a rectangular parallelepiped (or cylinder) to analyze the stress distribution during cooling, due to the mutual constraint ratio in the length direction and thickness direction of the sheet. The mutual restraint of the cuboid is weak, so the final deformation of the plate has a distortion phenomenon, which is more complicated than the deformation of the cuboid. However, the representation of the stress distribution should be based on the center of the large plane, and the stress perpendicular to the large plane is less than the stress parallel to the large plane. The actual quenched sheet material, on the large plane of the sheet, some of the two processing shapes (grooves) are asymmetrical, but this asymmetrical shape does not have a consistent correspondence to the amount of deformation of the quenching, indicating: The stress value in the thickness direction of the plate has little effect on the deformation.
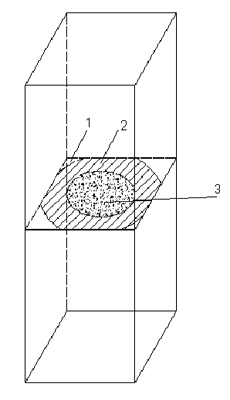
Figure 7, sheet cooling analysis model
In the high-pressure gas quenching and cooling process before the quenching is interrupted, the plate is mainly composed of thermal stress. The first cooling of the plate is the four corner regions of the plate, which causes shrinkage. Due to its independence, the deformation of the whole plate is affected. Not large, but if the interrupt quenching method is not used, an angular warping sometimes occurs after continuous quenching. The second cooling is at the area 2 of the plate, shrinking during cooling, because the cooling of the region 4 is slower at a higher temperature stage, preventing the shrinkage of the region 2, being subjected to tensile stress, and the region 4 is subjected to compressive stress, since the workpiece is at this time In the plastic phase, the area 2 may be elongated. After the cooling is continued until the quenching is interrupted, the region 4 also shrinks. Since the pre-cooling of the region 2 is elongated compared to the block tension, the tensile stress is generated for the region 4, and the final stress is the region 2 without considering the influence of the phase transition. Under compressive stress, zone 4 is subjected to tensile stress.
The phase transition stress distribution after the quenching is interrupted: first, the phase change occurs in the region 1, and the discontinuous tensile stress is generated in the region 2. Due to the slow cooling, the martensite transformed by the region 1 is subjected to the heat from the region 2 to cause self-tempering. Phenomenon, martensite precipitates ε-carbide, reduces volume expansion, tensile stress in region 2 increases MS [4], and region 2 undergoes martensite gradual transformation to offset tensile stress from the outside to the inside. A similar transition process and stress change process occurs between Zone 2 and Zone 4. Since the temperature near the MS point is slow, the phenomenon of "transition-----self-tempering-----transition" continues, and the structural stress of the transformation result is small, and the transition curves 1, 2, and 3 are continuously cooled. It can be seen that in the case of a slow cooling time of 50-100 min at room temperature, the temperature of the region 4 is around 200 ° C, and a small amount of bainite transformation occurs in the supercooled austenite, which reduces the volume expansion. This martensite-based multiphase structure has better toughness after tempering than a single tempered martensite structure. The amount of supercooled austenite in the region 4 of the sheet is much larger than that in the rest of the region from the MS point of the stress influence transition. This part of the retained austenite is distributed in the subsequent high temperature tempering, and has little effect on the deformation.
The distribution of thermal stress and tissue stress is opposite, offsetting each other. The residual stress in the sheet is small. Achieve the effect of reducing the quenching deformation of large plates.
During the process of interrupting the quenching and discharging, the measurement observation: the deformation of the plate when the quenching is interrupted is close to zero, indicating that when the thermal stress is affected, the stress is released better due to the higher temperature, and the plane deformation of the plate is not obviously caused. At 30 minutes after the tapping, the center of the large plane of the sheet is first recessed, restored at a later time, then turned to the reverse side and then restored. This phenomenon is repeated for 1-2 cycles, and the amount of depression in the middle of the plane is gradually reduced, and finally cooled to The amount of deformation at room temperature can reach the amount of deformation required by the technical requirements.
V. Conclusion
The large blanking template adopts interrupted quenching in the vacuum gas quenching furnace, which can solve the quenching deformation problem well.
References
[1] Mold Steel, Inc. and Daido Steel Limited. Information, Japan.
[2].YSS. High quality cold work die steel SLD (data 6), Japan, Hitachi Metals, Ltd. http://
[3]. Sanyo special steel co. ltd. Information, Japan.
[4]. [æ—¥] Mi Gu Mao, Zhu Jingyu and other translations, the generation of residual stress and countermeasures, Mechanical Industry Press, 1983.4.P166.
Previous page
Pull Out Faucet,Pull Out Sink Faucet,Hot Cold Pull Out Tap,Brass Pull Out Kitchen Faucet
Jiangmen Faer Sanitary Co.,Ltd , https://www.faersanitarys.com